Earned Value Management – How Could It Help Your Project?
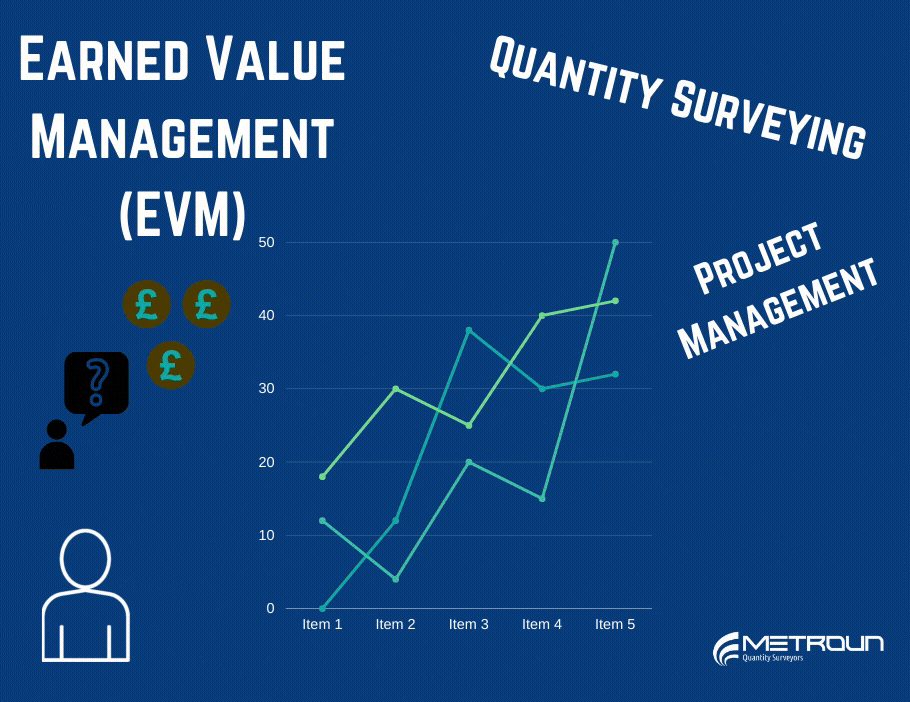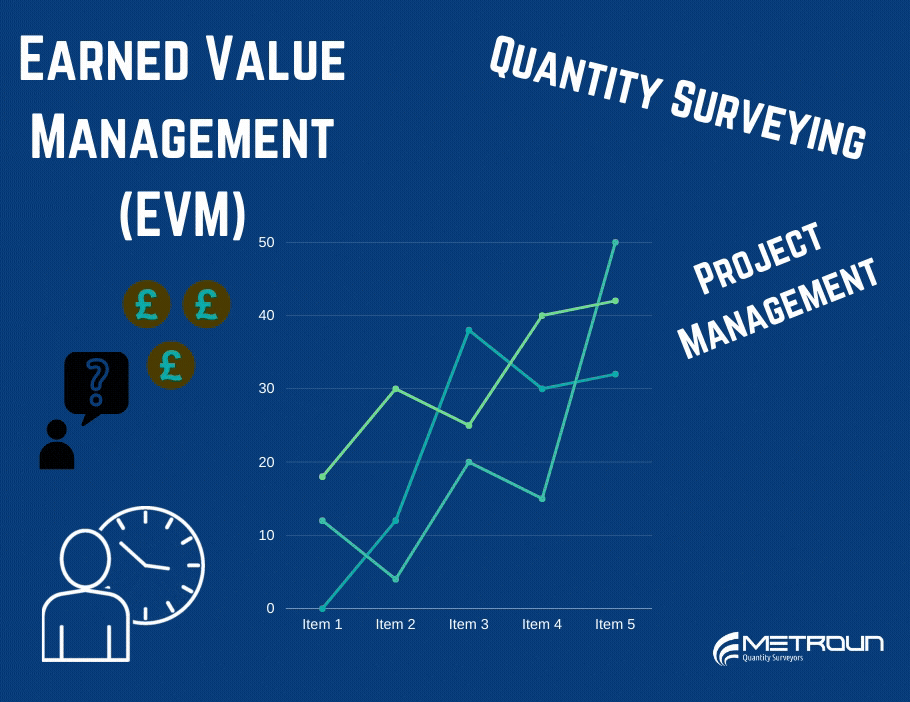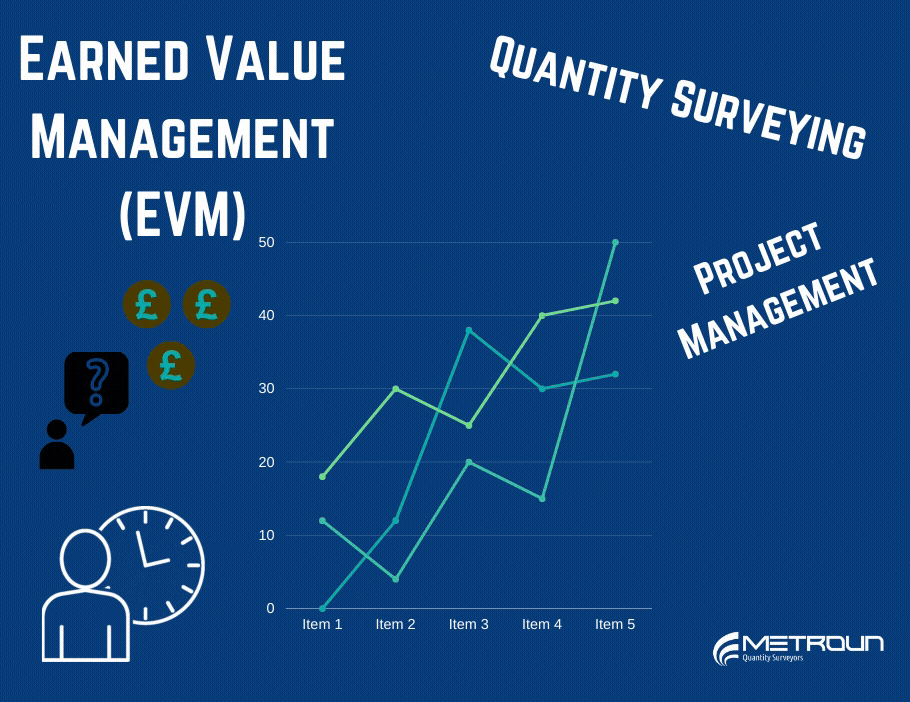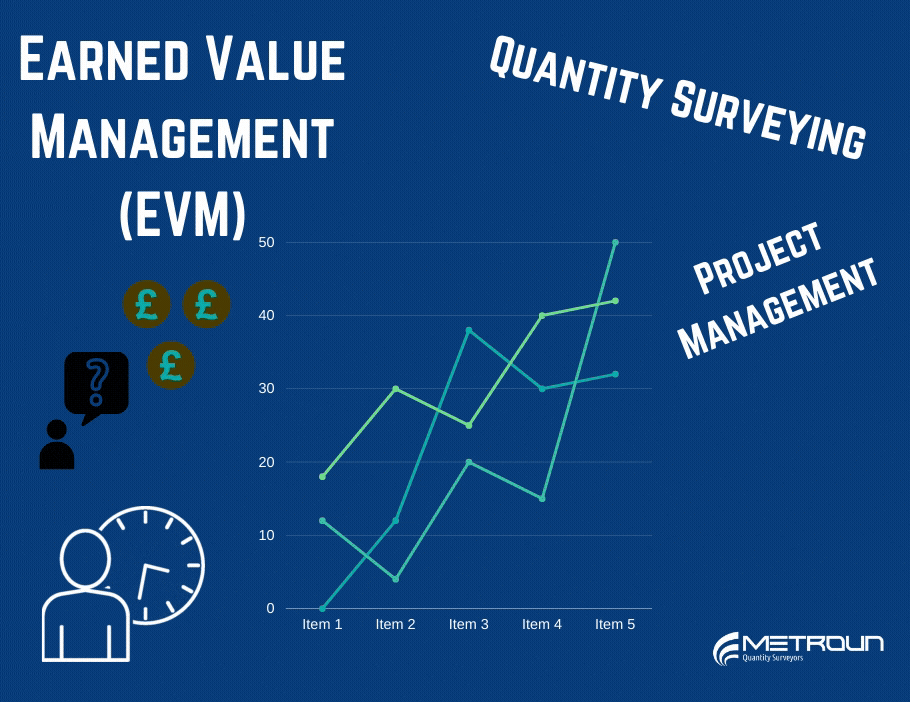
Earned Value Management is a performance metric which can be used in order to manage a project, by answering the
NEC3 & 4 What Is An Early Warning?

One thing you can guarantee on a construction project is you will face issues. However it is how these issues
7 Simple Reasons A Quantity Surveyor Can Save You Time, Money & Heartache.

When you need a sink installed, you hire a Plumber. When your car needs a repair, you hire a mechanic.
NEC Options – What Do They Mean?

How Our Roads Are Built

Roads are a relatively ancient invention for the modern human. The first mention of road building came was over 6000
IR35 – What is it? And what will the changes really mean?

Definitions (for the purpose of this article): Contractor: the individual who is granted work by the employer and operates either as self-employed, through their own limited company or through an agency (in which case, the onus would be on the agency to determine employment status). Company: the organisation who is acting as the employer and paying for services / expertise from the contractor. What is IR35? IR35 is a set of rules that applies to workers who provide their work through an intermediary party. The rules would apply to anyone who is contracting either under an umbrella company (agency) or through their own limited companies. The rules were essentially introduced in the year 2000 as a mechanism to combat tax avoidance. They are there to ensure that an individual contractor pays the equivalent tax and national insurance contributions as they would do if they were an actual employee, working for the company on their payroll and covering the same position / responsibilities. As we will discover though, at present, this is very rarely happening. How do current contractors escape high tax payments? The way contractors have traditionally set themselves up is to incorporate their own limited company where they are the sole employee. They pay themselves the minimum wage but come the end of the tax year, they take a big dividend payment which consequently incurs much lower tax implications. This is versus receiving the payments monthly and paying normallevels of income tax and National Insurance Contributions (NIC). The latest figures from HMRCshowed that due to this loophole, an extremely low 10% of contractors complied with the current IR35 rules leading to a very urgent calls for reform. What is the current state of the Construction Industry? Within the construction industry the use of contractors is very commonplace due to the natureof the work being so highly fragmented and working on contracts that only run for a certain amount of time, such as 12 months to build a new car park or 18 months to build a new housing complex. After this time, the expertise of the individual is no longer needed and so historically this has been a good way for companies to keep staff overheads down and move with any given workload. Equally, the contractor can demand a much higher rate of pay due tonot receiving the usual benefits working for a company permanently provides. Benefits to thecontractor: Benefits to the company: Due to the benefits listed above among others, the popularity and vast number of companies who use contractors, and indeed the number of individuals who choose to supply their services through an intermediary has been continually rising. Consequently, the construction industry has always seen a good balance of supply and demand in this area. What are the changes? Previously, the onus has been on the contractors limited company to determine the status of their employment for each individual assignment. The new rules mean that the onus will now be transferred from the contractor / freelancer to the company who actually employs them. If the company is found to be employing a worker through the contracting method and they are not declaring their true rate of pay (rather paying themselves minimum wage and collecting large dividend payments), then the company will face extremely large fines. This will be enforceable for failing to meet a statutory obligation. It will become the company’s responsibility to determine the employment status of their contractors. If it is deemed that the contractor is treated as a permanent employee (other thanthe fact they are being employed through their own private limited company), then the company is liable to pay all of the fees and tax contributions that they would otherwise need to pay if they employed the individual on a permanent basis on their normal payroll. Now, determining exact employment status is a notoriously ‘grey’ area and hard thing to do. Aquick search of the court cases surrounding this area show a vast number of separate battles, some with the contractor winning and some with them losing. A great place to start though would be where a business to business transaction (in this instance an employer paying a contractor for his services through an invoice), consists solely of that individuals’ wages and nothing else. When will the new rules be introduced and enforceable?
NEC3 & 4 What Is A Compensation Event?

If you’ve ever worked on an NEC Contract you would have heard the term Compensation Event (CE). If you haven’t heard the term, you may have heard of Relevant Events, used on other contracts like JCT. This article will aim to provide clarity on Compensation Events and provide you with some practical examples. Please click here for our selection of NEC tailored excel templates for download. “Compensation Events are events which are usually not the fault of the contractor and change the cost of the work, or the time needed to complete it. As a result, the prices, key dates or the completion date may be reassessed, and in many cases the contractor will be entitled to more time or money” – Fenwick Elliot. The purpose of a CE is to place the contractor into the position he was in before the event occurred. In other words, if an event caused a contractor to lose £2,000, the CE would aim to reimburse the loss incurred. Alternatively, an event may cause a delay to the Completion Dateor Key Date. A CE will aim to alter these dates, so the effect of the event has no impact how early or late a project or key date completion is met. Disclaimer: The assumptions within this article are based on a non-amended NEC3 Engineering and Construction Contract. The clauses and project stakeholders will vary on different projects. Examples of Compensation Events (NEC3) This list gives examples of specific CEs from clause 60.1 of NEC3: · The Employer does not allow access to the site by the access date shown on the Accepted Programme
What Is A PassivHaus / Passive House?

People in Britain have always used some type of device to heat their homes in the winter, whether this be
Remote Working – World Environment Day 2020

When we talk about the benefits of remote work, we normally talk about the benefits for people: for remote staff
How to Manage Risk Effectively in Construction

There are three main areas which must be considered for effective risk management as defined by Jaafari and Anderson (1995), starting with risk identification to risk analysis and finally risk response. As you will see throughout this article, dealing with risks collaboratively and using the mechanisms built into more collaborative constructions contracts makes this process a great deal easier and straight forward. Initially identifying the possible risks that may occur however, is of course extremelyproblematic in itself but a vital first step in risk management (Williams, 1995). The importance of such a task cannot be underestimated as a risk that is not identified cannot possibly be controlled, mitigated or managed (Bajaj, 1997). Despite the difficulties, there are mechanisms which allow this task to be controlled and completed successfully with a lot of the success hinging on the extent of collaboration between the parties involved. A way to achieve collaboration in the risk identification process is through a mechanism where the principle contractor involves the subcontractors early and also having input from the client in a procedure known as Early Contractor Involvement (ECI). The next stage of managing risks effectively is ‘risk analysis’. Part of analysing risks effectivelyalso includes consideration of quantifying them and the potential frequency, time frames and magnitude of the individual risk events (Williams, 1995). Much of the construction world recognises (as has the newer standard forms of contract, NEC3, JCT/CE etc.) the importance of balancing effectively and fairly apportioning the allocation of risk between the employer and contractor. It is generally understood that balancing risks fairly has a better chance of leading to reasonable prices and fewer disputes (Lane, 2005). Apportioning and allocating risks in an effective manner therefore, plays a vital role in regards to promoting collaborative practices and ultimately achieving project cost savings. The final stage of risk management is concerned with how the risks identified should be responded to. Again, the newer collaborative practices that are largely sought after by clients,desire the project team and different organisations who employ them, to share potential risks on a scheme accurately and promptly with the view to benefiting the overall construction project. This can be done through the Early Warning Notice process if using the NEC contract and regular progress meetings for example. However, do not despair… RM does not always have to be doom and gloom! An area of RM which is very often overlooked in the literature and equally on projects is identifying the risks which may actually present opportunities. The work by Hillson (2002) suggests 4 responses which can beused when dealing with opportunities versus risks as the same responses are notnecessarily effective for dealing with opportunities. These responses are: exploit; share; enhance or ignore. Incidentally, if risk and consequently identification of opportunities are managed effectively it could actually lead to a competitive advantage for firms rather than always seeing risks to be negative and detrimental to the project. The clear, close and intertwined relationship between collaboration and risk management andthe perceived advantages it can have on a scheme’s success, has led to many corners of the industry attempt to suggest different ways and techniques to improve collaboration and therefore by association risk management. Effectively managing risks could see the biggest impact on cost savings for most clients so rather than treating it as tick-box exercise it needs to be treated with the upmost respect! Find out more on NEC contracts with our post on Collaboration – A significant shift


